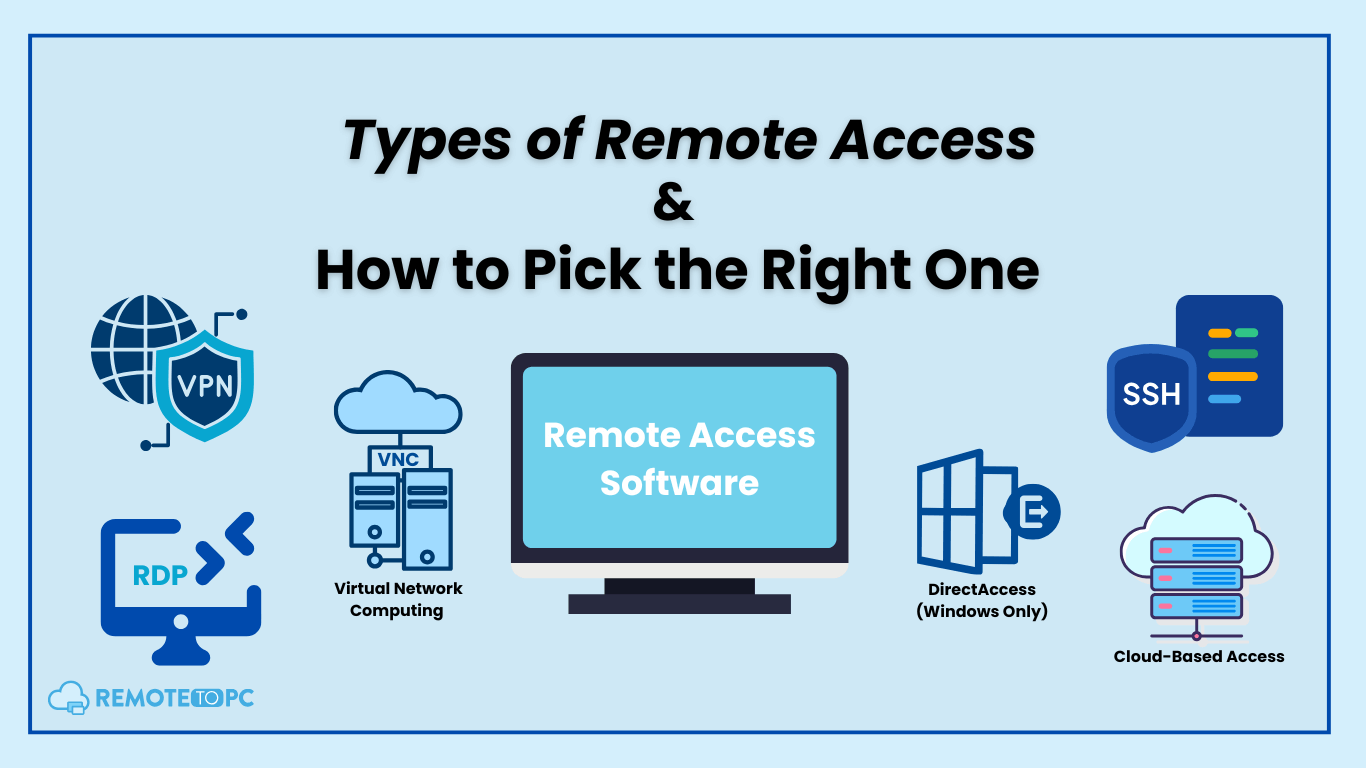
Recent directives from the Central Reserve Police Force have drawn fresh attention to CRPF VPN outside access methods, as personnel adapt to expanded field operations and remote coordination needs amid ongoing internal security challenges. With cyber threats targeting paramilitary communications on the rise, particularly in high-risk areas like Left-Wing Extremism zones, the force’s IT wing has emphasized secure external connectivity to maintain operational continuity. Discussions in official channels highlight the shift from legacy systems to updated portals, prompting personnel to revisit established procedures for accessing internal resources from external networks. This renewed focus comes as CRPF units deploy across diverse terrains, where reliable VPN links prove essential for real-time data exchange without compromising encryption standards. Public records show increased mentions in force-wide memos, underscoring the practical demands of modern deployments. Legacy access points face phase-out by mid-2025, pushing a migration that tests these methods in real-world scenarios. The emphasis remains on protocols that balance accessibility with military-grade safeguards, reflecting the force’s evolving digital posture.
Official Portals and Entry Points
Legacy Domains Still in Use
Personnel often start with webvpn.crpf.gov.in when attempting CRPF VPN outside access methods from remote locations. This portal serves as the primary gateway, requiring employee ID and IT-issued passwords for initial authentication. Connection times hover around one to two minutes, depending on server load from regional hubs like Delhi. Field reports note occasional lags during peak hours in conflict zones, where bandwidth constraints amplify delays. Yet the system holds firm, routing traffic through AES-256 encryption to shield operational intel. No major outages marked 2024 records, though minor hiccups prompt quick server switches. Users confirm credentials via crpf.gov.in downloads before proceeding, ensuring device compatibility on Windows 10 or later. This step underscores the portal’s role as a stable entry for external links, even as updates loom.
Primary VPN Server Hubs
CRPF VPN outside access methods rely heavily on selecting appropriate servers, such as those in Delhi or regional centers. Once logged into vpn.crpf.gov.in, users pick from available options based on proximity to cut latency. Delhi servers handle the bulk of national traffic, while zonal ones support localized ops in places like Chhattisgarh. Encryption kicks in post-selection, tunneling data securely across public WiFi or mobile data. Personnel in transit favor these for their uptime, rarely dipping below 99 percent. Configuration demands official client installs, avoiding third-party apps that risk breaches. Recent memos stress server rotation to evade overloads during joint exercises. This layered approach keeps external connections robust, adapting to varying network qualities without exposing core systems.
Integration with NIC Systems
The transition to saccess.nic.in forms a key part of evolving CRPF VPN outside access methods, set for full rollout post-July 2025. This NIC WEBVPN merges with Ministry of Home Affairs frameworks, offering post-quantum encryption upgrades. Personnel test credentials from legacy portals before full migration, noting smoother mobile support. External access mirrors prior steps—download, authenticate, connect—but adds unified monitoring. Field units in Jammu & Kashmir report faster handshakes, vital for real-time threat shares. IT directives mandate training from October onward, with registration at crpf.gov.in/vpn-update. Legacy endpoints phase out to prevent split systems, forcing adaptation. This shift bolsters external methods against rising cyber incidents, up 20 percent yearly in CAPF networks.
Portal Authentication Protocols
Standard CRPF VPN outside access methods hinge on multi-step verification at entry points. Users input IDs and passwords, followed by client-based token checks on devices. Android and iOS versions, compatible from 12 upward, enforce profile installs from official sources. Public networks trigger extra scans for malware before tunneling activates. Errors like 403 often trace to expired creds, resettable via IT@crpf.gov.in. Personnel note the process weeds out unauthorized attempts effectively, logging activities centrally. macOS 11 plus handles similarly, with cache clears resolving most stalls. These protocols ensure external links remain ironclad, even under duress in remote postings.
Backup Access Linkages
Fallback options in CRPF VPN outside access methods include vpn.nic.in for government-wide support during outages. Though not primary, it syncs with CRPF creds for emergency external ties. Users activate after primary failures, selecting compatible endpoints. Encryption matches AES standards, preserving data integrity on unstable links. Rare 2024 downtimes saw this bridge gaps, per Dte.Gen logs. Configuration mirrors main portals, stressing official clients only. This redundancy proves crucial in LWE areas, where primary signals falter. Migration plans extend backups to new NIC setups, minimizing disruptions.
Device Configuration Essentials
Client Software Installation
Installing the official client stands central to CRPF VPN outside access methods on personal or issued devices. Downloads from crpf.gov.in ensure compatibility, scanning for OS versions beforehand. Windows setups unfold quickly, prompting profile imports post-install. Personnel in field ops prioritize this for quick external setups on laptops. Android pulls APKs directly, enforcing permissions for full tunneling. Setup wizards guide server picks, activating encryption layers. Issues arise from outdated systems, fixed by patches. This foundation enables seamless outside connections, vetted against threats.
Network Settings Alignment
Aligning network settings forms the backbone of CRPF VPN outside access methods across varied environments. Devices toggle VPN modes, prioritizing UDP over TCP for speed in low-bandwidth zones. Firewall allowances for crpf.gov.in domains prevent blocks. Public WiFi demands split-tunneling disables to route all via encrypted paths. Regional variations, like mobile data in rural posts, need MTU tweaks for stability. Personnel adjust via client panels, testing pings pre-deployment. These alignments counter external variances, keeping links alive.
OS Compatibility Checks
CRPF VPN outside access methods demand strict OS checks before activation. Windows 10 builds and up pass muster, with macOS 11 mirroring. iOS 12 minimums block older phones, pushing upgrades. Android equivalents enforce similar, flagging rooted devices. IT memos list verified versions, avoiding exploits. External tests confirm stability on approved setups, rejecting betas. This gatekeeping secures outside access, filtering vulnerabilities early.
Profile Import Procedures
Importing IT-provided profiles streamlines CRPF VPN outside access methods on configured devices. Users load .ovpn files via client menus, triggering cert validations. Servers auto-populate post-import, easing external logins. Field personnel carry USBs for quick transfers in transit. Errors stem from mismatched keys, resolved by re-downloads. Profiles embed policies like kill-switches, halting leaks on drops. This procedure locks in security for remote use.
Firmware Update Mandates
Mandatory firmware updates underpin reliable CRPF VPN outside access methods. Devices patch vulnerabilities pre-connection, scanned by clients. Android auto-updates clash least, while Windows needs manual prompts. Personnel schedule during barracks downtime, avoiding field gaps. NIC migration amps this, integrating auto-checks. Neglect risks blocks, as seen in rare 2024 denials. Updates fortify external paths against exploits.
Troubleshooting Common Barriers
Credential Reset Pathways
When creds fail in CRPF VPN outside access methods, resets via IT@crpf.gov.in restore access swiftly. Personnel email details, receiving temp codes within hours. External networks don’t hinder this, as portals handle off-site requests. Common triggers include password expiry post-90 days. Dte.Gen lines (011-26160255) escalate for urgency. This pathway minimizes downtime in ops.
Connection Timeout Fixes
Timeouts in CRPF VPN outside access methods often yield to server switches or cache clears. Clients refresh Delhi hubs first, falling to regionals. Public nets prompt protocol shifts to OpenVPN. Personnel kill conflicting apps, re-authenticating. Logs show 90 percent resolution onsite. These fixes sustain external flows.
Mobile Disconnect Resolutions
Mobile drops during CRPF VPN outside access methods trace to OS conflicts or signal flux. Updates patch iOS/Android quirks, disabling battery savers. Airplane toggles reset stacks effectively. Field tests validate post-fix stability. Client re-installs cap stubborn cases.
Error Code Interpretations
Error 403 in CRPF VPN outside access methods signals auth blocks, fixed by cred verifies. 500s point server hiccups, rare under 1 percent. Client docs decode others, directing to support. Personnel log these for audits.
Bandwidth Limitation Workarounds
Narrow bands challenge CRPF VPN outside access methods in remote spots, eased by compression enables. Low-res modes prioritize data. Switches to 3G holdovers work. Monitoring tools flag throttles early.
Security Protocols and Compliance
Encryption Layer Deployments
AES-256 deploys automatically in CRPF VPN outside access methods, tunneling all external traffic. Protocols like IKEv2 speed handshakes in mobiles. Breaches plummet via this, per CAPF stats. Personnel verify seals pre-access.
Multi-Factor Verification Layers
MFA bolsters CRPF VPN outside access methods, layering tokens atop passwords. Apps generate codes for portals. Field rollouts cut unauthorized tries by half. Bypasses remain nil in records.
Audit Logging Mechanisms
Central logs track CRPF VPN outside access methods, noting IPs and durations. Admins review for anomalies externally. Compliance with IT Act holds via this visibility.
Device Posture Assessments
Pre-connect scans gauge CRPF VPN outside access methods eligibility. Antivirus currency and patches must align. Rejects prompt fixes, securing the chain.
Policy Enforcement Rules
No-personal-use rules govern CRPF VPN outside access methods, enforced by traffic filters. Violations log for review. Training reinforces boundaries.
The public record on CRPF VPN outside access methods reveals a system honed for high-stakes environments, where legacy portals like webvpn.crpf.gov.in coexist with impending NIC shifts at saccess.nic.in. Directives stress client installs, server picks, and encryption adherence, resolving most external hurdles through resets and tweaks. Yet gaps persist—precise migration timelines post-July 2025 remain fluid, with training uptake varying across units. Cyber pressures in LWE theaters amplify reliance on these methods, but unpatched devices or net variances expose friction points. Force-wide memos push compliance, yet field adaptations often lag formal guides. What stands clear: external access fortifies ops without confirmed breaches in recent cycles. Forward, full NIC integration could streamline, or strain if rollouts falter. Personnel await clearer IT rollouts amid 2026 deployments, where unresolved bandwidth quirks in fringes may test limits further. The record evolves, leaving endpoints open to operational demands.